阅读声明:我个人是个 Linux 小白,写博客只是记录下日常工作中的一些问题和解决方案,如果文章中出现错误还请大佬勿喷
1、什么是 LVM ? 关于 LVM 的概念和说明,可以参考文章 LVM——让Linux磁盘空间的弹性管理 - 知乎 (zhihu.com) 作为所有操作后
这里只简单介绍一些相关概念
LVM 简介:
LVM(Logical Volume Manager),中文名称叫 逻辑卷管理,是在物理 磁盘/分区上 做整合再划分逻辑分区的机制(或者说磁盘管理技术)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 +-----------------------------------------------+
相关概念:
PV(Physical Volume):物理卷,在磁盘分区的基础上建立
VG(Volume Group):卷组,管理/整合 多个 PV
LV(Logical Volume):逻辑卷,在 VG 的基础上划分的逻辑分区
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 +-----------------------------------------------+
我个人理解: LVM 就是个将多个物理磁盘或者分区整合为一个逻辑磁盘再分区的机制/技术,这样比传统的磁盘分区更易用,并且将多个磁盘整合为一个逻辑上磁盘来使用可以突破单个物理磁盘的容量限制
2、LVM 扩容过程
所有操作都需要 root 权限,请在 root 用户下进行或者使用具有 root 权限的用户进行操作
! ! ! ! ! !
2.1、原因 由于个人喜欢在日常生活中写点小项目和代码,所以在公司内网的 ESXI 上建了个 Ubuntu 20.04 Server 作为开发服务器,公司的代码存放在上面,个人代码存储在自己的笔记本上。
今天照旧用 VS Code 远程到开发服务器上写代码时提示存储空间不够,故需要扩容,但是扩容过程一波三折,写篇文章记录下,以后碰到相关问题时可以参考
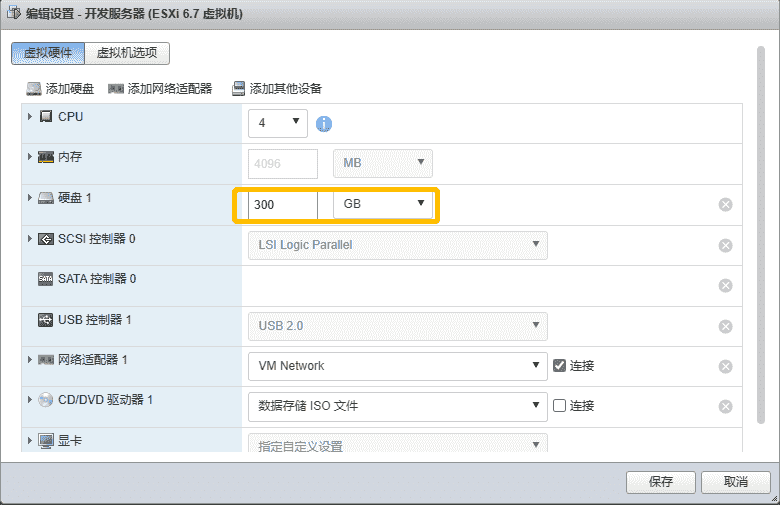
2.2、增加虚拟机的磁盘容量 首先在 ESXI 管理面板上增加虚拟机的容量
我这里的原容量为 100G 现改为 300G
如果修改不了,你可能需要将虚拟机关机后修改再将虚拟机开机
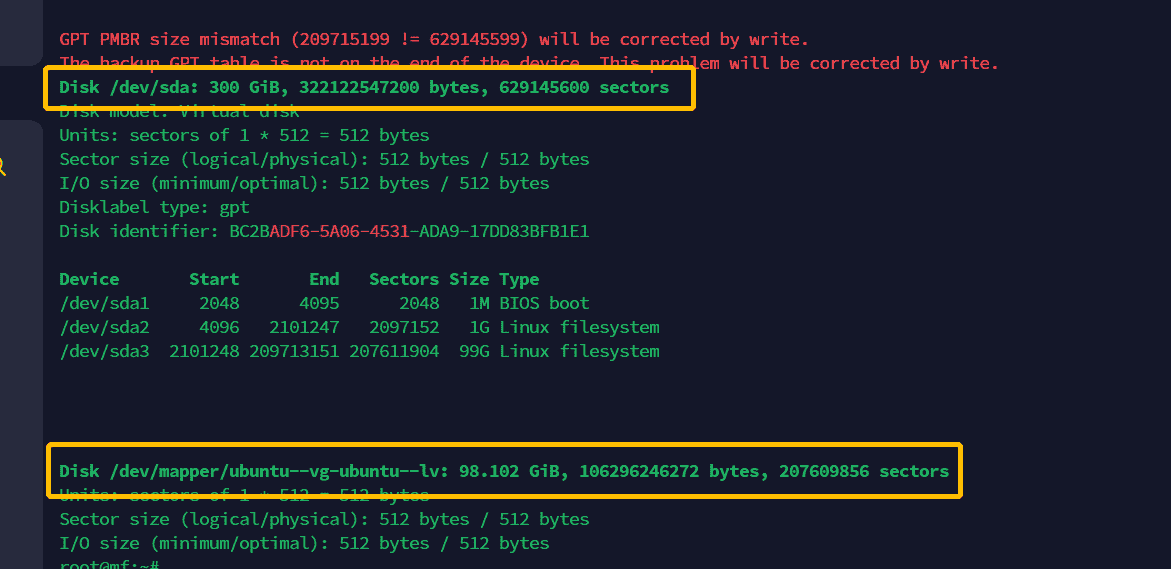
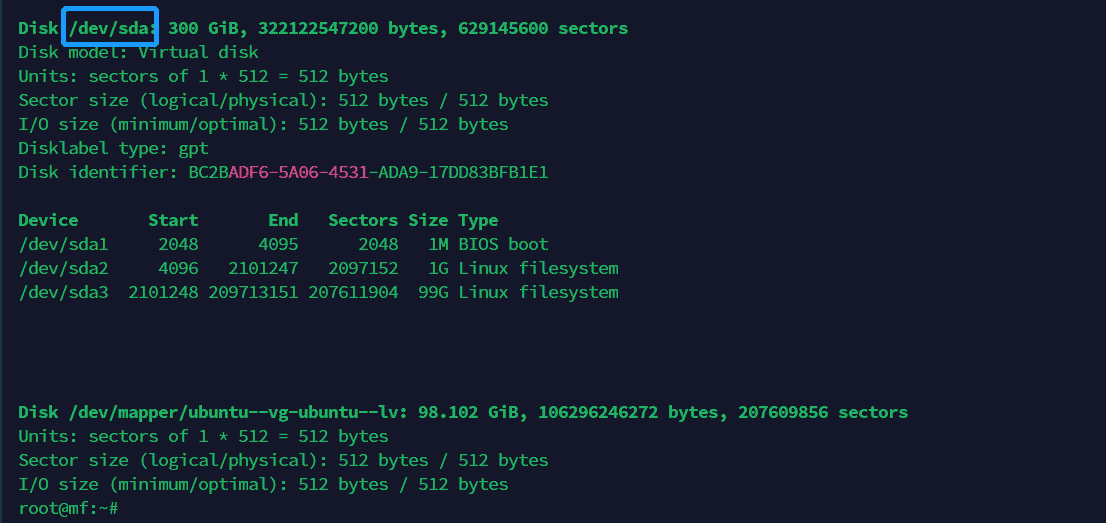
2.3、在空闲空间上建立 PV(物理卷) 2.3.1、查看当前分区信息 使用命令 fdisk -l 查看当前物理磁盘的分区信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 root@mf:~type : gpt
可以看到在 ESXI 中的修改生效了,磁盘空间已经是 300G
虽然磁盘大小改变了,但是我们的 LVM 的逻辑分区大小依旧是 100G 的空间
在介绍 LVM 的时候我们说过,LV(逻辑卷) 是从 VG(卷组) 中划分出来的,而 VG(卷组) 的容量又是其管理的一个或者多个 PV(物理卷)的总和
所以增加 LV(逻辑卷)的前提那肯定是增加 VG(卷组)下 PV(物理卷)的容量或者添加新的 PV(物理卷)来增加 VG(卷组)的容量,只有 VG(卷组)的容量增加了,才有多余的空间划分给 LV(逻辑卷)
所以现在需要做的就是将磁盘的空闲空间(也就是 300G - 100G = 200G)初始化为 PV(物理卷)然后添加到 VG(卷组) 中去
2.3.2、创建新分区 使用命令 fdisk /dev/sda 将磁盘的空闲空间划分为新的分区
需要注意:/dev/sda 是我本地磁盘的名称,你的磁盘名称不一定是这个,如不一致需要替换为你自己的磁盘名称
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 root@mf:~in memory only, until you decide to write them.command .for help ): ptype : gptfor help ): ntype 'Linux filesystem' and of size 200 GiB.for help ): ptype : gptfor help ): w
2.3.3、将新分区初始化为 PV(物理卷) 使用命令 pvcreate /dev/sda4 将新建的分区初始化为 PV(物理卷)
1 2 root@mf:~"/dev/sda4" successfully created.
使用命令 pvscan 查看当前有那些 PV(物理卷),
1 2 3 4 root@mf:~in use: 1 [<99.00 GiB] / in no VG: 1 [200.00 GiB]
2.3.4、将 PV(物理卷)添加到 VG(卷组)中 使用命令 vgdisplay 查看当前卷组信息:
字段
说明
VG Name ubuntu-vgVG 名称为 ubuntu-vg
Alloc PE Size 25343 / <99.00 GiB已经分配的容量 100G 左右
Free PE / Size 0 / 0可分配的容量 0G
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 root@mf:~read /write
使用命令 vgextend ubuntu-vg /dev/sda4 将新建的 PV(物理卷)/dev/sda4 添加到 VG(卷组) ubuntu-vg 中
1 2 root@mf:~"ubuntu-vg" successfully extended
使用命令 vgdisplay 再次查看当前卷组信息:
字段
说明
VG Name ubuntu-vgVG 名称为 ubuntu-vg
Alloc PE Size 25343 / <99.00 GiB已分配的容量 100G 左右
Free PE / Size 0 / 0可分配的容量 200G 左右
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 root@mf:~"ubuntu-vg" successfully extendedread /write
可以看到 VG(卷组)中多出了 200G 的可分配容量,这时 VG 的容量已经拓展好了,接下来就是将 VG(卷组)的容量划分到 LV(逻辑卷)上了
2.3.5、将 VG(卷组)的可分配容量划分到 LV(逻辑卷)中 使用命令,lvextend -l +100%FREE /dev/ubuntu-vg/ubuntu-lv VG(卷组)中的所有可分配容量全部划分到 LV(逻辑卷)/dev/ubuntu-vg/ubuntu-lv 中
1 2 3 root@mf:~
2.3.6、同步文件系统容量到内核 做完所有操作后,需要使用命令 resize2fs /dev/ubuntu-vg/ubuntu-lv 将 LV(逻辑卷)的信息同步到内核中,否则你的逻辑卷的容量大小将不会改变
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 root@mf:~
使用 df -h 命令查看 LV(逻辑卷)大小
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 root@mf:~
可以看到 LV(逻辑卷)/dev/mapper/ubuntu--vg-ubuntu--lv 的大小已从开始的 100G 增加到了 300G